LifeLock Bug Exposed Millions of Customer Email Addresses
Facebook stock falls 24 percent on forecast for slowing growth, rising expenses
July 25, 2018AMD second-quarter revenue, profit boosted by EPYC, Ryzen sales
July 25, 2018Identity theft protection firm LifeLock — a company that’s built a name for itself based on the promise of helping consumers protect their identities online — may have actually exposed customers to additional attacks from ID thieves and phishers. The company just fixed a vulnerability on its site that allowed anyone with a Web browser to index email addresses associated with millions of customer accounts, or to unsubscribe users from all communications from the company.
The upshot of this weakness is that cyber criminals could harvest the data and use it in targeted phishing campaigns that spoof LifeLock’s brand. Of course, phishers could spam the entire world looking for LifeLock customers without the aid of this flaw, but nevertheless the design of the company’s site suggests that whoever put it together lacked a basic understanding of Web site authentication and security.
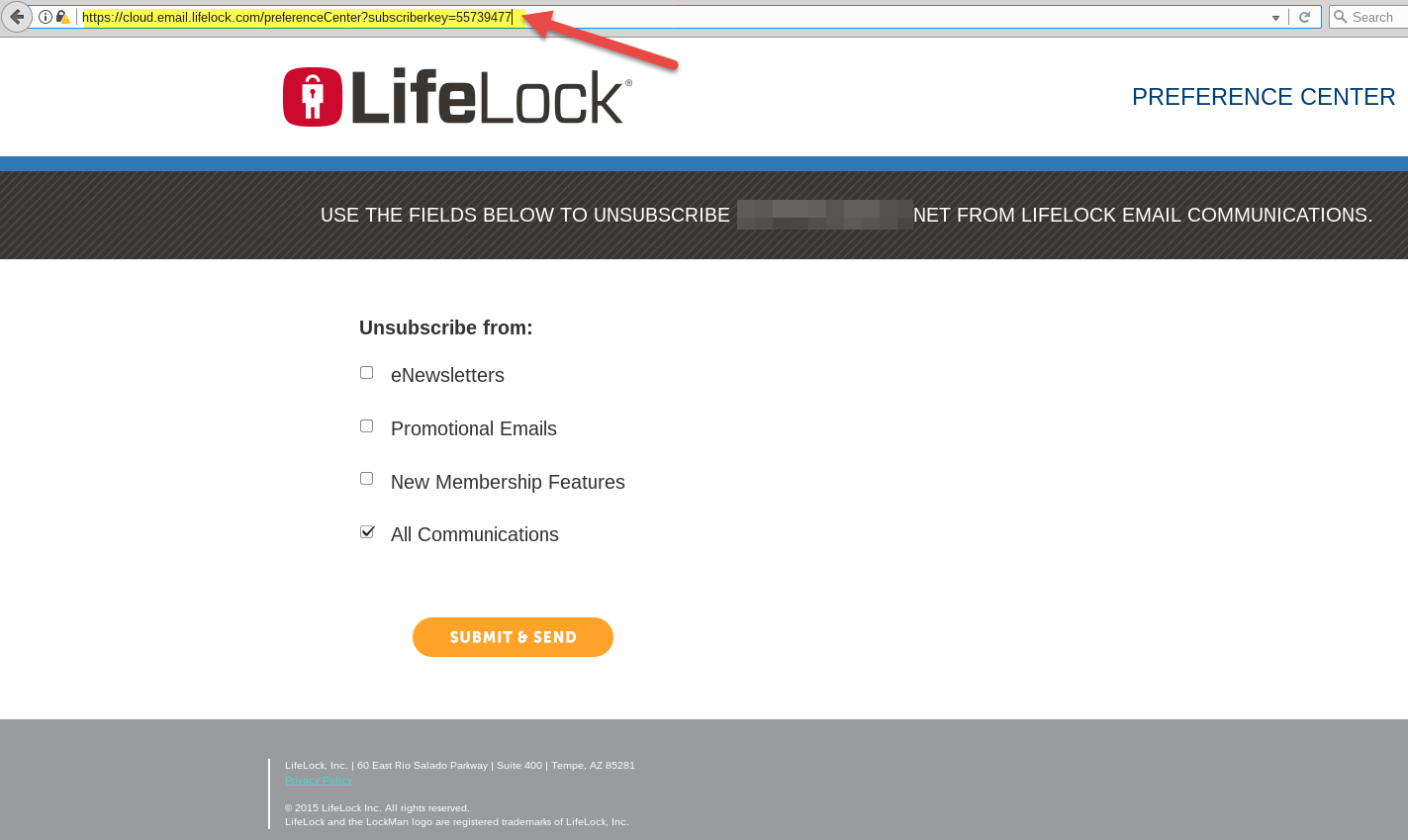
LifeLock’s Web site exposed customer email addresses by tying each customer account to a numeric “subscriberkey” that could be easily enumerated. Pictured above is customer number 55,739,477. Click to enlarge.
Pictured above is a redacted screen shot of one such record (click the image to enlarge). Notice how the format of the link in the browser address bar ends with the text “subscriberkey=” followed by a number. Each number corresponds to a customer record, and the records appear to be sequential. Translation: It would be trivial to write a simple script that pulls down the email address of every LifeLock subscriber.
Security firm Symantec, which acquired LifeLock in November 2016 for $2.3 billion, took LifeLock.com offline shortly after being contacted by KrebsOnSecurity. According to LifeLock’s marketing literature, the company has more than 55 million customer accounts.
KrebsOnSecurity was alerted to the glaring flaw by Nathan Reese, a 42-year-old freelance security researcher based in Atlanta who is also a former LifeLock subscriber. Reese said he discovered the data leak after receiving an email to the address he had previously used at LifeLock, and that the message offered him a discount for renewing his membership.
Clicking the “unsubscribe” link at the bottom of the email brought up a page showing his subscriber key, which was in the 55 million ballpark (55739477, to be exact). From there, Reese said, he wrote a proof-of-concept script that began sequencing numbers and pulling down email addresses. Reese said he stopped the script after it enumerated approximately 70 emails because he didn’t want to set off alarm bells at LifeLock.
“If I were a bad guy, I would definitely target your customers with a phishing attack because I know two things about them,” Reese said. “That they’re a LifeLock customer and that I have those customers’ email addresses. That’s a pretty sharp spear for my spear phishing right there. Plus, I definitely think the target market of LifeLock is someone who is easily spooked by the specter of cybercrime.”
LifeLock’s Web site is currently offline.
Misconfigurations like the one described above are some of the most common ways that companies leak customer data, but they’re also among the most preventable. Earlier this year, KrebsOnSecurity broke a story about a similar flaw at Panerabread.com, which exposed tens of millions of customer records — including names, email and physical addresses, birthdays and the last four digits of the customer’s credit card.
